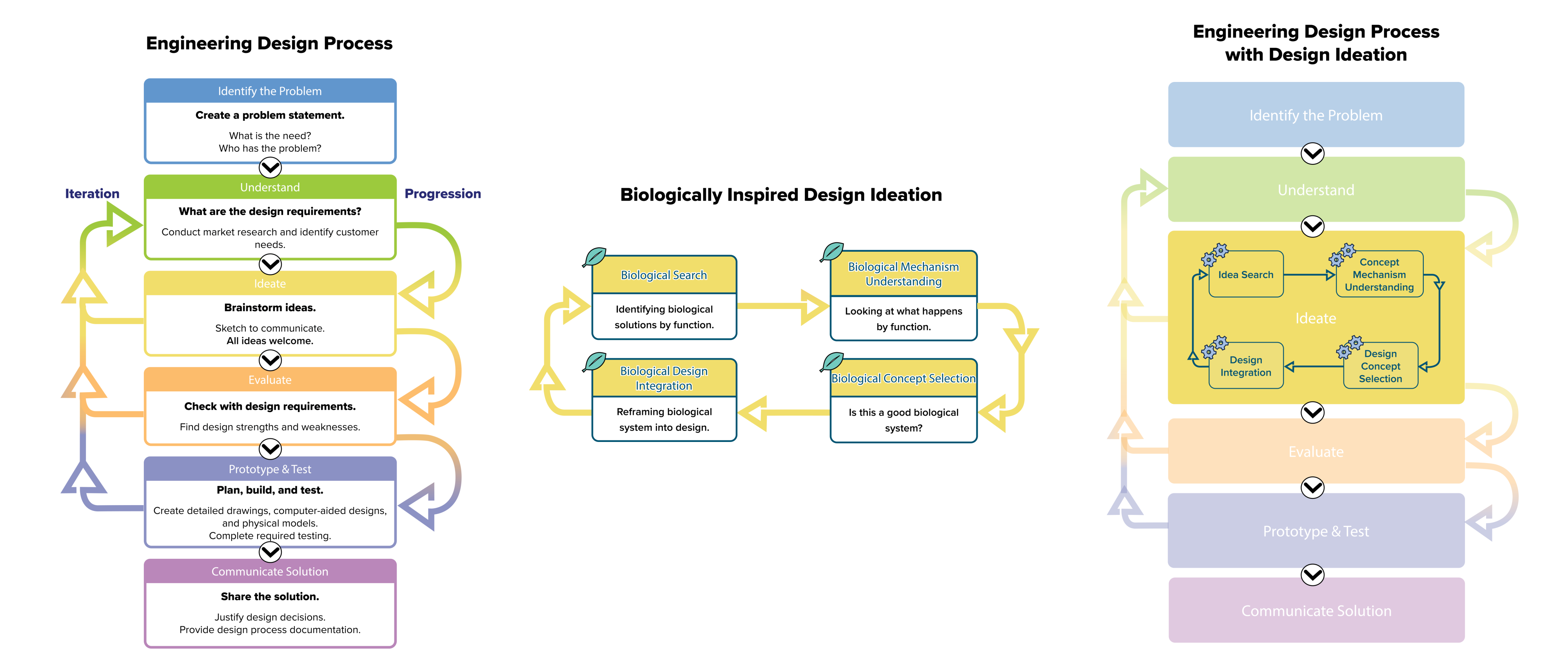
Biologically inspired design (BID) leverages what we already know about biological systems to provide a source of new, often more sustainable, design ideas to help address 21st Century design problems. In BIRDEE, we focus on the integration of biological design patterns in the ideation phase of the EDP. To effectively access the biological world, we need to start before ideation - at the problem definition phase - to ensure that problems descriptions facilitate access to and analysis of biological systems.
As students engage in problem-solving via the engineering design process (EDP) they integrate biologically inspired design (BID) into the EDP by leveraging analogical design tools, such as the 4-box method, that facilitate a transfer of biological strategies to design challenges. These tools scaffold key engineering design skills of problem understanding and design ideation. Moreover, the categories of the 4-box method provide indexes for the investigation of biological objects, enabling easier application of biological solutions to future engineering problems.
Students work to:
- understand the requirements of the problem or challenge
- identify possible investigations that would help answer their questions
- identify potential biological strategies for their problem or challenge
- develop and conduct investigations into biologically inspired solutions
- physically prototype their solutions; iteratively redesign their solutions to improve outcomes and communicate and defend their final solutions to an audience of their peers
| EDP Integration | Stage of the EDP | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identify the Problem | Understand | Ideate | Evaluate | Prototype and Test | Communicate Solution | ||||||
| Lesson | Identify | Write a Problem Statement | Define Requirements | SFM | Science behind the problem | Brainstorming Ideas | Conceptual Design | Evaluate Requirements | Prototype | Test Prototype | Create or give a presentation |
| 1.1.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.1.2. | |||||||||||
| 1.1.3. | |||||||||||
| 1.1.4. | |||||||||||
| 1.1.5. | |||||||||||
| 1.2.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.2.2. | |||||||||||
| 1.2.3. | |||||||||||
| 1.2.4. | |||||||||||
| 1.2.5. | |||||||||||
| EDP Integration | Stage of the EDP | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identify the Problem | Understand | Ideate | Evaluate | Prototype and Test | Communicate Solution | ||||||
| Lesson | Identify | Write a Problem Statement | Define Requirements | SFM | Science behind the problem | Brainstorming Ideas | Conceptual Design | Evaluate Requirements | Prototype | Test Prototype | Create or give a presentation |
| 1.3.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.3.2. | |||||||||||
| 1.3.3. | |||||||||||
| 1.3.4. | |||||||||||
| 1.3.5. | |||||||||||
| 1.4.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.4.2. | |||||||||||
| 1.4.3. | |||||||||||
| 1.4.4. | |||||||||||
| 1.4.5. | |||||||||||
| 1.5.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.5.2. | |||||||||||
| 1.5.3. | |||||||||||
| 1.5.4. | |||||||||||
| 1.5.5. | |||||||||||
| 1.6.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.6.2. | |||||||||||
| 1.6.3. | |||||||||||
| 1.6.4. | |||||||||||
| 1.6.5. | |||||||||||
| 1.7.1. | |||||||||||
| 1.7.2. | |||||||||||